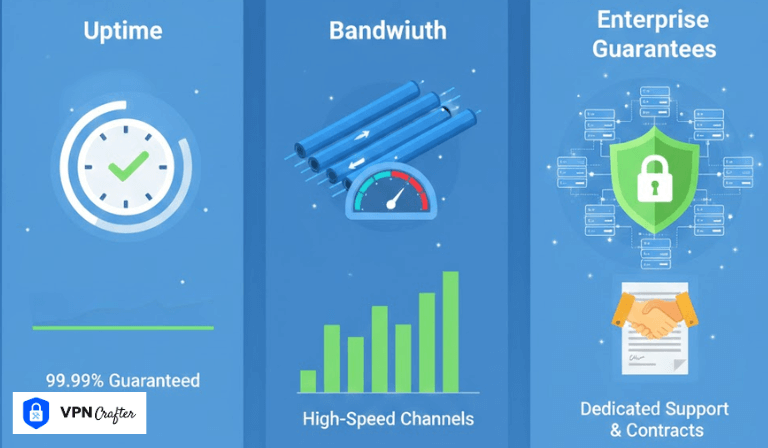
Enterprises do not buy VPNs the way consumers do. A consumer VPN wins on price, app design, or streaming access. An enterprise VPN wins or loses based on VPN SLA uptime and bandwidth guarantees.
Downtime costs real money. Throttled connections stall operations. A single outage can interrupt payroll systems, cloud access, customer support, or internal communications across continents. Decision-makers understand this risk, which explains why feature lists matter less than enforceable guarantees.
Marketing pages promise “99.9% uptime.” Procurement teams ask tougher questions. How is uptime measured? What happens during peak hours? Where is the accountability written down?
Those answers live inside the SLA, not the landing page.
1. What an SLA Means in VPN Development
A Service Level Agreement defines measurable performance commitments between a VPN provider and its customer. Unlike general SaaS tools, VPN SLAs touch network reliability, throughput, security enforcement, and response timelines.
VPN SLAs typically cover:
- Network uptime commitments
- Bandwidth availability and allocation models
- Incident response and remediation timelines
- Security enforcement guarantees
Legal and financial implications follow. Missed SLAs can trigger service credits, contract termination, or compliance violations. For enterprises, SLAs are risk management tools, not fine print.
2. Uptime Guarantees: What 99.9% Actually Means
Numbers sound impressive until the math becomes real.
A 99.9% uptime allowance permits over 43 minutes of downtime per month. At 99.99%, downtime drops to about 4 minutes. The difference determines whether global teams experience interruptions weekly or yearly.
Advertised uptime often excludes maintenance windows, regional failures, or upstream provider outages. Enforced uptime accounts for all service-impacting events.
Reliable VPN SLA uptime and bandwidth guarantees rely on infrastructure, not promises.
3. Enterprise-Grade Uptime Architecture
High uptime does not happen by accident. It is engineered.
Enterprise VPN platforms use:
- Multi-region server clusters to isolate failures
- Intelligent load balancing to distribute traffic
- Automatic rerouting when a node degrades
- Zero single-point-of-failure design principles
This architecture ensures users remain connected even during hardware failures or regional disruptions. Enterprises expect resilience by default, not as an upgrade.
4. Bandwidth Allocation Explained
Bandwidth defines usability under load. Many VPNs operate on shared bandwidth models, which degrade performance during peak hours.
Enterprise-grade VPNs offer:
- Dedicated or prioritized bandwidth pools
- Region-aware traffic allocation
- Burst capacity during demand spikes
A white label VPN for business built on enterprise infrastructure avoids congestion traps that cripple consumer-grade networks.
5. Why Bandwidth Guarantees Matter to Enterprises
Modern enterprises run on real-time connectivity.
Stable bandwidth supports:
- Video conferencing and VoIP reliability
- Secure access to internal systems
- Large file transfers across regions
- Performance consistency for distributed teams
Bandwidth instability creates friction that employees notice instantly. Strong VPN SLA uptime and bandwidth guarantees protect productivity and trust.
6. Throttling vs Fair Usage Policies
Some VPN providers throttle silently. Others enforce transparent fair usage policies tied to SLAs.
Enterprise VPNs define:
- Maximum throughput per user or region
- Clear thresholds for heavy usage
- Guaranteed minimum performance levels
SLA-backed delivery beats best-effort networking every time. Enterprises value predictability more than unlimited claims.
7. Monitoring, Reporting, and SLA Enforcement
SLAs only matter when measured.
Enterprise VPN providers deliver:
- Real-time uptime dashboards
- Bandwidth usage reports
- Incident logs and resolution timelines
Penalties and service credits enforce accountability. Transparency builds trust. Weak reporting erodes confidence quickly.
8. Security SLAs: More Than Just Encryption
Security commitments extend beyond AES-256 encryption headlines.
Strong VPN SLAs include:
- Kill switch reliability guarantees
- DNS and IP leak prevention enforcement
- Incident response windows
- Breach notification procedures
A VPN for security must prove operational discipline, not just protocol support.
9. How SLAs Influence Vendor Trust and Procurement
Procurement teams evaluate vendors through risk lenses.
They compare:
- SLA clarity versus vague assurances
- Enforcement mechanisms
- Historical uptime performance
- Infrastructure ownership
Pricing rarely wins alone. Weak SLA language often signals weak engineering maturity.
10. SLA Differences in Custom vs White Label VPN Development
This distinction matters.
White Label VPN vs Custom VPN approaches differ significantly in risk exposure.
Custom VPN builds require:
- Independent infrastructure design
- Ongoing capacity planning
- Internal security audits
- SLA enforcement from scratch
White-Label VPN Development leverages pre-validated infrastructure with proven SLA benchmarks. Enterprises prefer predictability over experimentation, especially during early growth.
11. Aligning SLAs With Business Risk and Compliance
Regulated industries demand strict alignment.
VPN SLAs often support:
- SOC 2 and ISO frameworks
- Internal IT risk management policies
- Jurisdictional data handling rules
Enterprises match SLA tiers to operational criticality. Mission-critical systems require higher guarantees than general browsing traffic.
12. Questions Enterprises Should Ask Before Signing
Smart buyers ask direct questions:
- How is uptime measured and reported?
- Are bandwidth guarantees per user or per region?
- What escalation paths exist during outages?
- How fast does support respond during incidents?
Clear answers separate serious providers from marketing-first vendors.
White Label VPN for Business: Why Enterprises and Founders Choose It
Companies looking to launch your own VPN brand face the same decision logic enterprises use.
A white label VPN for business offers:
- Enterprise-grade SLA frameworks
- Proven uptime architecture
- Predictable scaling costs
- Faster time to market
Founders exploring how to start a VPN business quickly discover that infrastructure risk kills momentum. White label VPN solutions remove that risk while preserving brand control.
How White Label VPN Works in Practice
A white label VPN solution provides:
- Fully managed backend infrastructure
- SLA-backed uptime and bandwidth
- Multi-tenant architecture
- Custom branding and pricing control
Teams focus on go-to-market strategy instead of server failures.
Learning how to use white label VPN platforms becomes a growth exercise, not a survival challenge.
Revenue Models for Your White Label VPN Business
Strong SLAs unlock monetization.
Common revenue models include:
- Subscription tiers tied to SLA levels
- B2B licensing and reselling
- Enterprise bundles with dedicated bandwidth
- Regional pricing strategies
Reliable infrastructure makes recurring revenue predictable.
Final Words: SLAs Are the Real Differentiator
Features attract attention. Guarantees close deals. VPN SLA uptime and bandwidth guarantees define whether a VPN survives enterprise scrutiny or fades into noise. Infrastructure-backed commitments reduce operational risk, protect brand equity, and support long-term growth.
Organizations choosing VPN partners should prioritize enforceable SLAs over flashy claims. Founders planning to start your own VPN brand should do the same. The market rewards reliability. Everything else is optional.